how to draw a distribution box plot in sas A box-and-whiskers plot displays the mean, quartiles, and minimum and maximum observations for a group. Throughout this chapter, this type of plot, which can contain one or more box-and . They chose white metal siding for the exterior and a very clean and minimalistic geometry for the building.
0 · sas sgplot vbox by group
1 · sas boxplot sgplot
2 · sas boxplot example
3 · sas boxplot by group
4 · sas box plot interpretation
5 · sas box and whisker plot
6 · proc boxplot sas example
7 · how to create a box and whisker plot in sas
$17.99
A box-and-whiskers plot displays the mean, quartiles, and minimum and maximum observations for a group. Throughout this chapter, this type of plot, which can contain one or more box-and . A Box Plot is very popular to view the distribution of an analysis variable with one or more classifiers. Also, everyone wants to customize the graph in different ways. One recent request was for creating a box plot by .
The histogram reveals features of the ratio distribution, such as its skewness and the peak at 0.175, which are not evident from the tables in the previous example. The following statements create the histogram:About Distribution Plots. You can use the SGPLOT and SGPANEL procedures to produce plots that characterize the frequency or the distribution of your data. The plot statements include many options for controlling how the output is . The following SAS statements combine the pre- and post-program scores and use a box plot to visualize the distribution of the scores. Because this is a matched-pair study, you can draw lines that connect the scores of the .You can use the SGPLOT and SGPANEL procedures to produce plots that characterize the frequency or the distribution of your data. The plot statements include many options for .
You can create a box plot to examine the distribution of power output for each day. The following statements create the box plot shown in Figure 18.1. symbol color = salmon h = .8;
The PLOT statement requests a box-and-whiskers plot for each group of data. After the keyword PLOT, you specify the analysis variable (in this case, KWatts ), followed by an asterisk and the . How to Create Boxplots by Group in SAS. Boxplots are useful for quickly visualizing the five-number summary of a dataset, which includes: The following example shows how to create grouped boxplots in SAS to visualize .
I am using SAO OnDemand for Academics. In SAS Studio, I have tried using the Box Plot under Graph, but it does not allow for side-by-side box plots. Therefore, I am not sure where to find this capability. I have looked .
This simple visualization uses the VBOX statement in PROC SGPLOT. As I explained previously, you can use the CATEGORY= and GROUP= options to display the distribution of calcium for the joint levels of the two .
The resulting graph uses box plots to show the schematic distribution of each of the joint levels of the two categorical variables. (The second EFFECTPLOT statement creates an "interaction plot" that shows the raw . Thanks for your quick reply. But this is not what i want, this is an example for "Box Plot with Multiple Connect Lines". What I need is the two groups are showing in different formats, blue group is a box plot, but the red group only needs to connect mean, does not need box. And i want these two groups in one figure. Thanks.
A box plot summarizes the data and indicates the median, upper and lower quartiles, and minimum and maximum values. The plot provides a quick visual summary that easily shows center, spread, range, and any outliers. The SGPLOT and SGPANEL procedures have separate statements for creating horizontal and vertical box plots. The main goal for that article was display of statistics with a Box Plot. Often we want to view the data by a discrete variable along with its distribution. Starting with SAS 9.40M3, we can overlay a VBOX on the Scatter plot, as shown on the right. Here the box plot is offset to the right from the data.
Hi. I am comparing two groups from a trial. I want to visually show the distribution of each group. I would like combine the two histogram with two boxplots in one, Basically I want it to look like the output from a ttest but without kernel and normal lines. Google is . A Stem and Leaf plot is a visual that can help quickly visualize the distribution of the data. This graph was particularly useful before the advent of modern statistical graphs including the Histogram and Box Plot. One nice feature of the plot is .
How to Style Box Plot in SAS. FILLATTRS option sets the fill color of the boxes to red with a transparency of 0.5.; LINEATTRS option sets the color of the lines around the boxes to red.; WHISKERATTRS option sets the color of the whiskers (lines that extend from the boxes) to red.; The LABEL= option in the xaxis and yaxis statements specify the labels for the x-axis and y . Otherwise, the stem-and-leaf plot appears. The stem-and-leaf plot is like a horizontal bar chart in that both plots provide a method to visualize the overall distribution of the data. The stem-and-leaf plot provides more detail because each point in the plot represents an individual data value. About Box Plots; About Density Plots; About Histograms; About Distribution Plots. You can use the SGPLOT and SGPANEL procedures to produce plots that characterize the frequency or the distribution of your data. The plot statements include many options for controlling how the output is displayed.
Let's create some fake data. Assume that a set of students take a test, then take the enrichment program, then retake the test. The following SAS DATA step defines the data. A call to PROC SGPLOT visualizes the distribution of the test scores before the enrichment program. I use a strip plot overlayed on a box plot to visualize these data.
Hi, You have two options - at the very least. 1). turn the ODS graphics off by simply saying: "ods graphics off" before your plot. 2).Assuming that you use SAS 9.2 or higher (hence you automatically get the ODS Graphics) you can modify the .This example shows a horizontal box plot. proc sgplot data=sashelp.heart; title "Cholesterol Distribution by Weight Class"; hbox cholesterol / category=weight_status; run; Previous Page
Box Plot. The box plot, also known as a schematic box plot, appears beside the stem-and-leaf plot. Both plots use the same vertical scale. The box plot provides a visual summary of the data and identifies outliers. The bottom and top edges of the box correspond to the sample 25th (Q1) and 75th (Q3) percentiles.specifies the type of distribution curve that is used for the density plot. Specify one of the following keywords: NORMAL < (normal-opts)> specifies a normal density estimate, with a mean and a standard deviation. normal-opts can be one or more of the following values: MU= numeric-value
So the answer to my question is: Yes, I want to draw line further out than the data actually exists within the 1.5 IQR. The first time I was introduced to Box-and-whisker plots the rule was the whiskers indicate the data, not the calculation. The purpose of a box-and-whisker is to show distribution of data in a concise form.The box-and-whisker plot, referred to as a box plot, was first proposed by Tukey in 1977. Figure 1: Box & Whisker Diagram, Tukey, 1977. Tukey’s original box-and-whisker plot used the less familiar hinge instead of upper and lower quantile measurements. The .Each of the 10 box-and-whiskers plots describes the variable KWatts for a particular day. The plot elements and the statistics they represent are as follows: The length of the box represents the interquartile range (the distance between the th and th percentiles). The symbol in the box interior represents the group mean.
The issue is with the results in Figure 24.3.4 as part of Example 24.3 Creating Various Styles of Box-and-Whisker plots in the SAS/Stat user's manual. The problem is with the whiskers in the figure. The text states that the interquartile range is the difference between the 25th and 75 quartile (the height of the box). Hi All, I am trying to create side by side violin plots (with 2 plots representing percentages of 2 groups) , with a boxplot overlay (the boxplot within showing mean, IQR and confidence intervals). Although I've been able to create the violin plot on its own, I am not sure how to create the boxpl.Base SAS® 9.4 Procedures Guide: Statistical Procedures, Sixth Edition documentation.sas.com. SAS® Help Center. Customer Support SAS Documentation. SAS® 9.4 and SAS® Viya® 3.5 Programming Documentation | SAS 9.4 / Viya 3.5. PDF EPUB Feedback. Welcome to SAS Programming Documentation for SAS® 9.4 and SAS® Viya® 3.5 .
variables. are the variables for which Q-Q plots are created. If you specify a VAR statement, the variables must also be listed in the VAR statement. Otherwise, the variables can be any numeric variables in the input data set. If you do not specify a list of variables, then by default the procedure creates a Q-Q plot for each variable listed in the VAR statement, or for each . In a vertical box plot the box upper and lower values are the 3rd and 1st quartiles. When you have a dichotomous variable with exactly two values 1 and 0, the "3rd quartile" will be "1st quartile" and the first will be 0. So any plot of C_1 or such will be pretty much the same: a box one unit high so that makes no sense. A previous article shows how to use a scatter plot to visualize the average SAT scores for all high schools in North Carolina.The schools are grouped by school districts and ranked according to the median value of the schools in the district. For the school districts that have many schools, the markers might overlap, which makes it difficult to visualize the .Instead, the SYMBOL statement and options specified after the slash (/) in the PLOT statement control its appearance. The GSTYLE system option restores the use of ODS styles for subsequent high-resolution graphics output. For more information about SYMBOL statements, see SAS/GRAPH: Reference. The resulting box plot is shown in Figure 24.3.
Box plots summarize the distribution of a continuous variable. You can display multiple box plots in a single graph by specifying a categorical variable. The resulting graph shows the distribution of subpopulations, such as different experimental groups. In the SGPLOT procedure, you can use the CATEGORY= option on the VBOX
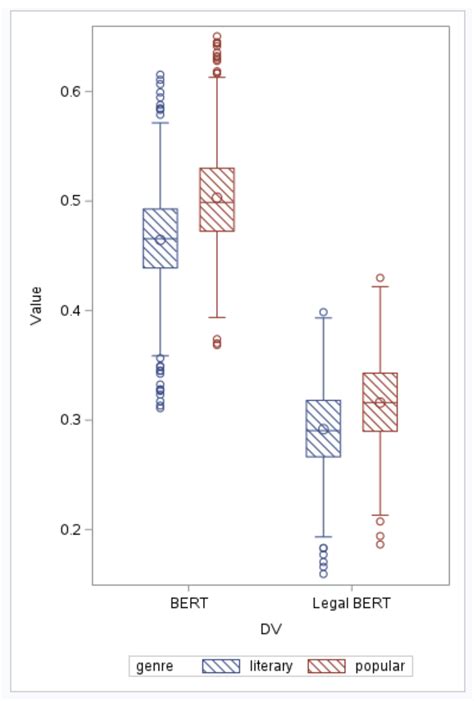
sas sgplot vbox by group
sas boxplot sgplot
$19.99
how to draw a distribution box plot in sas|sas boxplot by group